Back
The New Crypto Mandate:Five Strategic Steps Your Finance Team Must Take to Prepare for Project Crypto

Gana Misra
Dec 6, 2025
SEC
Updates

The cryptocurrency revolution has moved from the margins to the mainstream. As institutional adoption accelerates and regulatory frameworks solidify globally, finance teams face a transformative challenge that extends far beyond simple asset management. Project Crypto represents a fundamental restructuring of treasury operations, cross-border payment systems, and financial reporting standards. The question is no longer whether your organization will engage with digital assets, but how prepared your finance team is to manage them effectively, compliantly, and strategically.
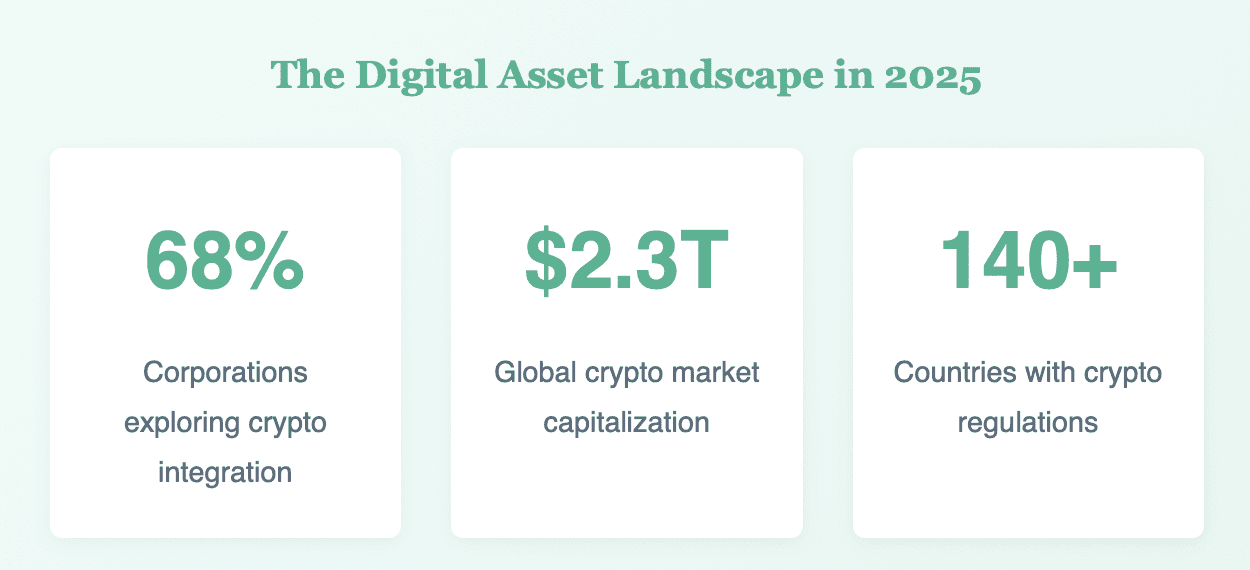
1
Establish a Comprehensive Regulatory Framework
The regulatory environment for digital assets continues to evolve at an unprecedented pace, creating a complex compliance landscape that varies significantly across jurisdictions. Finance teams must develop sophisticated frameworks that address not only current regulatory requirements but also anticipate emerging standards in anti-money laundering, securities classification, and consumer protection.
Understanding the nuances between different regulatory regimes—from the SEC's approach to digital securities in the United States to the MiCA framework in the European Union—is critical for organizations operating internationally. The consequences of non-compliance extend beyond financial penalties to include reputational damage and operational restrictions that can fundamentally limit business opportunities.
STRATEGIC IMPLEMENTATION PRIORITIES
Conduct comprehensive regulatory audits across all jurisdictions where your organization operates or plans to engage in crypto activities
Implement robust Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) protocols specifically designed for blockchain transaction monitoring
Establish a dedicated compliance function with expertise bridging traditional financial regulation and digital asset innovation
Develop clear internal classification systems for different crypto asset types (payment tokens, utility tokens, security tokens, stablecoins)
Build proactive relationships with regulatory authorities and participate in industry working groups shaping future standards

2
Upgrade Your Technology Infrastructure
Traditional financial systems were architected for centralized, permission-based networks with clear intermediaries and standardized settlement periods. Cryptocurrency operates on fundamentally different principles—decentralized validation, cryptographic security, and near-instantaneous settlement. This paradigm shift necessitates a comprehensive technology overhaul that extends across custody solutions, accounting systems, and transaction monitoring capabilities.
The security requirements alone represent a departure from conventional practices. While traditional banking relies on institutional safeguards and regulatory backstops, cryptocurrency custody demands that organizations become their own security architects, implementing multi-signature protocols, hardware security modules, and sophisticated key management systems that eliminate single points of failure.

INFRASTRUCTURE MODERNIZATION ROADMAP
Deploy enterprise-grade crypto accounting platforms such as Cryptio, Bitwave, or Lukka that integrate seamlessly with existing ERP systems
Implement segregated custody solutions distinguishing between hot wallets for operational needs and cold storage for long-term holdings
Establish automated reconciliation protocols that can handle the high transaction volumes and fractional denominations typical in crypto operations
Integrate blockchain analytics capabilities for real-time transaction monitoring, address screening, and risk scoring
Develop comprehensive disaster recovery procedures specifically addressing cryptocurrency's unique characteristics, including private key backup and recovery protocols
3
Develop Robust Accounting and Tax Strategies
Cryptocurrency accounting presents challenges that extend well beyond traditional asset management. The classification of digital assets remains subject to interpretation across different accounting standards, with significant implications for balance sheet presentation, income recognition, and impairment testing. Organizations must navigate questions of fair value measurement in highly volatile markets, revenue recognition for crypto-denominated transactions, and the appropriate treatment of emerging asset classes such as NFTs and tokenized securities.
Tax considerations add another layer of complexity. In most jurisdictions, cryptocurrency is treated as property rather than currency, triggering capital gains calculations on every transaction—including routine operational activities. This creates substantial record-keeping requirements and necessitates sophisticated cost-basis tracking methodologies that can handle complex scenarios such as hard forks, airdrops, staking rewards, and decentralized finance transactions.
ACCOUNTING FRAMEWORK ESSENTIALS
Establish clear valuation methodologies aligned with applicable accounting standards (GAAP, IFRS, or local equivalents), addressing both measurement at initial recognition and subsequent reporting periods
Implement granular cost-basis tracking systems capable of managing multiple acquisition dates, prices, and transaction types across potentially thousands of individual units
Develop comprehensive impairment testing procedures for crypto assets, recognizing that current accounting standards may require write-downs that cannot be subsequently reversed
Create specialized processes for recognizing and measuring income from diverse sources including trading gains, mining operations, staking rewards, and DeFi yield farming
Build tax strategies addressing jurisdiction-specific rules for different transaction types, including wash sale considerations, like-kind exchange limitations, and loss harvesting opportunities
Establish relationships with auditors possessing deep cryptocurrency expertise and staying current with evolving guidance from standard-setting bodies

4
Implement Comprehensive Risk Management Protocols
The risk profile of cryptocurrency operations differs fundamentally from traditional financial activities, introducing exposure categories that legacy risk frameworks were never designed to address. Operational risks include the irreversibility of transactions, the catastrophic impact of private key loss or compromise, and the dependency on external infrastructure such as blockchain networks and exchange platforms over which organizations have limited control.
Market risks in cryptocurrency extend beyond typical volatility concerns. Digital assets can experience price movements of 20% or more in single trading sessions, liquidity can evaporate rapidly during market stress, and correlation patterns with traditional assets remain unstable and difficult to predict. These characteristics demand risk management approaches that combine quantitative rigor with qualitative judgment about an asset class still defining its role in the broader financial system.

RISK MITIGATION FRAMEWORK
Establish multi-signature wallet architectures requiring consensus among multiple authorized individuals for all material transactions, eliminating single points of failure
Implement position sizing rules that limit cryptocurrency exposure relative to total treasury holdings, with clear escalation procedures for exceeding established thresholds
Develop comprehensive vendor assessment frameworks specifically addressing the unique risks of cryptocurrency service providers, including proof-of-reserves verification and insurance coverage evaluation
Create detailed incident response playbooks covering scenarios such as exchange failures, smart contract vulnerabilities, private key compromises, and extreme market volatility
Secure specialized insurance coverage for digital assets, recognizing that traditional crime and fidelity policies typically exclude cryptocurrency-related losses
Establish governance structures defining clear approval authorities for different transaction types, investment decisions, and risk limit modifications
5
Invest in Education and Talent Development
The sophistication required to manage cryptocurrency operations effectively cannot be acquired through conventional finance education alone. Blockchain technology, cryptographic principles, decentralized finance mechanisms, and the rapidly evolving regulatory landscape represent a knowledge domain that intersects technology, finance, and law in ways that traditional finance roles rarely encounter.
Organizations face a fundamental choice: develop internal expertise through intensive training programs or acquire talent from the cryptocurrency industry. The optimal approach typically involves both strategies—upskilling existing team members who understand the organization's operations, risk appetite, and culture while simultaneously bringing in specialists who can provide depth in specific areas such as blockchain architecture, smart contract auditing, or DeFi protocol analysis.
CAPABILITY BUILDING STRATEGY
Sponsor team members to complete professional certification programs in blockchain technology and digital asset management from recognized institutions
Recruit experienced cryptocurrency finance professionals for senior positions, ensuring they possess both technical blockchain knowledge and traditional financial expertise
Establish advisory relationships with specialized consulting firms that can provide guidance on complex technical, regulatory, and strategic questions
Create internal knowledge-sharing mechanisms such as lunch-and-learn sessions, crypto working groups, and documentation repositories that democratize specialized knowledge across the finance function
Invest in attendance at major blockchain and cryptocurrency conferences, ensuring team members maintain awareness of emerging trends, technologies, and regulatory developments
Develop mentorship programs pairing cryptocurrency-experienced professionals with traditional finance staff, facilitating knowledge transfer and building organizational capability
Establish relationships with academic institutions and research organizations conducting cutting-edge work in blockchain economics and digital asset markets

Moving Forward: From Preparation to Implementation
Project Crypto is not a theoretical exercise or a distant possibility—it represents the present reality for an increasing number of organizations across industries. Those that approach digital asset integration thoughtfully and systematically will discover opportunities for treasury optimization, operational efficiency gains, and competitive differentiation that were simply unavailable in the traditional financial system.
The five strategic imperatives outlined in this framework provide a foundation, but successful implementation requires adaptation to your organization's specific circumstances, risk tolerance, and strategic objectives. Begin with pilot programs that allow controlled experimentation and learning. Establish clear success metrics that extend beyond simple return calculations to include operational effectiveness, compliance quality, and capability development.
Most importantly, recognize that cryptocurrency adoption is a journey of continuous learning and adaptation rather than a one-time project with a defined endpoint. The technology will continue evolving, regulations will mature and shift, and market structures will develop in ways we cannot fully predict today. Organizations that build adaptive capabilities, maintain epistemic humility, and invest consistently in their teams will be best positioned not just for Project Crypto, but for the broader digital transformation reshaping the global financial architecture.
The critical question facing your finance team: Which capability gap will you address first, and how will you measure progress toward cryptocurrency readiness?